GOATS User Guide
Introduction
Are you a Singaporean private tutor who has trouble keeping track of your student's details? Ever thought of having an easier and more efficient way to keep track of students and their parents? Introducing GOATS!
The Greatest Offline Addressbook for Teaching Students, or GOATS, is an offline desktop app designed for your administrative needs for private tutoring. GOATS does not only help you keep track of students information such as phone number, grades and education level, it also helps you access the students' parents information as well. GOATS also boasts features such as archiving, sorting and pinning contacts to make sure you organise and find contacts quickly and easily.
The GOATS app is intended for private tutors who possess knowledge of basic computer skills (such as installing, downloading and navigating files). In addition, GOATS is optimised for fast typists with prior experience in using the Command Line Interface (CLI). So, if you can type fast, GOATS can get your student management tasks done faster than traditional Address Book applications!
This User Guide provides a guide of how to set up GOATS and a description of useful commands that you can use.
Please first ensure that you meet the Minimum System Requirements in order to run GOATS.
After that, if you are a beginner or a first-time user, we recommend that you start with the Quick Start section. Otherwise, feel free to explore the various features either through the Command Summary or the Table of Contents.
This User Guide also includes highlighted sections to aid in your reading:
Notes: This section will contain information that is useful to know.
Tips: This section will contain recommendations for users to consider.
Examples: This section will contain examples of different ways a command could be used.
Caution: This section will contain warnings for certain commands and information that are vital for GOATS to run smoothly. Do ensure that you take special note of the contents here.
Minimum System Requirements
Please ensure that you have the following:
- A computer running on Windows, macOS or Linux.
- Ensure you have Java 17 or above installed on your computer.
- To check if you have Java 17 installed on your computer, follow the following steps:
- Open a Terminal Emulator.
- On Windows: Open up
Windows Powershellfrom the list of applications. - On Linux: Click on the
Activitiesitem at the top left of the screen, then type interminaland open the displayed application. - On macOS: Type in
terminalin the search field in the list of applications and open the displayed application.
- On Windows: Open up
- Type in the following command:
java -version. - If the response contains
java version "17.x.x"or higher, you’re all set! - Otherwise, please refer to this guide to download Java 17.
- Open a Terminal Emulator.
- To check if you have Java 17 installed on your computer, follow the following steps:
Quick Start
- Download the latest
.jarfile from here. - Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for GOATS.
- Open a Terminal Emulator. For those unfamiliar with opening a terminal emulator, follow the instructions in the Minimum System Requirements.
- Type in the following command to navigate to the GOATS home folder:
cd, followed by the location of your home folder. e.g.cd Documents/GOATS_Home_Folder - Type in the following command to launch the GOATS application:
java -jar GOATS.jarA GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
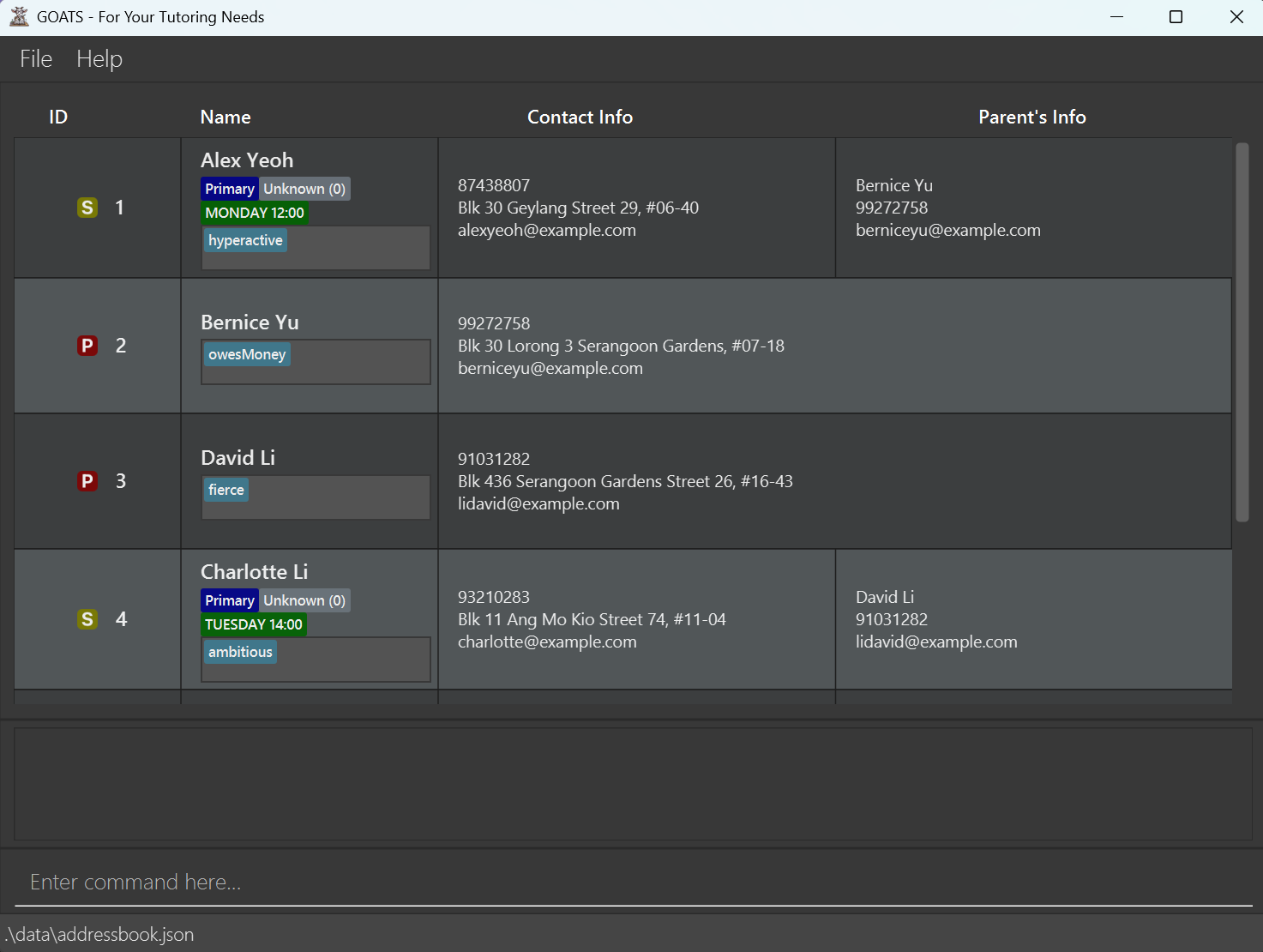
6. You are ready to start using GOATS! Try out some example commands in the command box and press Enter to execute them.
Some example commands you can try:
list: Lists all contacts.addstudent n/James Ho p/91715131 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 134665 edu/primary lt/wed:13:00 t/friend: Adds a student namedJames Hoin GOATS.delete 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list.clear: Deletes all contacts.exit: Exits the app.
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Command summary
| Action | Format (Example) |
|---|---|
| Add Parent | addparent n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… (addparent n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01) |
| Add Student | addstudent n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS lt/LESSON_TIME edu/EDUCATION_LEVEL [t/TAG]… (addstudent n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 134665 edu/primary lt/wed:13:00 t/friend t/colleague) |
| Archive | archive INDEX [MORE_INDICES]… (archive 1 2 3 4) |
| Assign Grade | grade INDEX g/GRADE_INDEX (grade 1 g/1) |
| Clear | clear |
| Delete | delete INDEX [MORE_INDICES]… (delete 1 2 3 4) |
| Edit | edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [lt/LESSON_TIME] [edu/EDUCATION_LEVEL] [t/TAG]… (edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com) |
| Exit | exit |
| Find | find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]… (find James Jake) |
| Find By Lesson Day | findday KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]… (findday Tuesday) |
| Find By Tag | findtag KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]… (findtag math science) |
| Help | help |
| Link Student To Parent | link ch/STUDENT_NAME pa/PARENT_NAME (link ch/James Ho pa/Jane Doe) |
| List | list |
| List Archive | listarchive |
| List Students | liststudents |
| List Parents | listparents |
| Pin | pin INDEX [MORE_INDICES]… (pin 1 2 3 4) |
| Sort | sort |
| Unarchive | unarchive INDEX [MORE_INDICES]… (unarchive 1 2 3 4) |
| Unlink Student from Parent | unlink ch/STUDENT_NAME (unlink ch/James Ho) |
| Unpin | unpin INDEX [MORE_INDICES]… (unpin 1 2 3 4) |
Features
Command Format
| Notation | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Words in UPPER_CASE | These are the parameters to be supplied by the user. Parameters for all commands are valid regardless of the order they are supplied in | For example, in addstudent n/NAME, NAME is a parameter which can be used as addstudent n/John Doe If the command specifies n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER, the writing the input in this order, p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAME is also acceptable. |
| Items in square brackets | These are optional parameters. | For example, n/NAME [t/TAG] can be used as n/John Doe t/friend or as n/John Doe. |
| Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters will be ignored. | If any parameters are given for commands that do not require them, the given parameters will be ignored. | Some examples of commands that do not take in parameters include: - help - list - clear - exit If list n/Betsy is entered, then the n/Betsy portion wil be ignored. |
Notes about the command format:
Separate commands cannot be strung together into one input
e.g. Entering the input archive 1 pin 2 list instead of entering commands separately, archive 1, pin 2, list
If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
Command Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
NAME | The contact's name. It should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank. Names should be unique For names with non-alphanumeric characters, we recommend replacing the non-alphanumeric portion with an alphanumeric alternative. e.g. 's/o' can be replaced with 'son of' | - James Ho - Jane Doe |
PHONE_NUMBER | The contact's phone number. It should only contain numbers, and it should be 3 to 17 digits long. | - 99228833 - 6598986767 |
EMAIL | The contact's email address. It should be of the format local-part@domain and adhere to the following constraints: - The local-part should only contain alphanumeric characters and these special characters, excluding the parentheses, (+_.-). The local-part may not start or end with any special characters. - This is followed by a '@' and then a domain name. The domain name is made up of domain labels separated by periods. The domain name must: - end with a domain label at least 2 characters long - have each domain label start and end with alphanumeric characters - have each domain label consist of alphanumeric characters, separated only by hyphens, if any. | - web@dev - jamesho@gmail.com |
ADDRESS | The contact's residential address. It can take any values, and it should not be blank. | - 123, Clementi Rd, 123465 - Blk 417, Tampines St 71, S510666 |
TAG | A single word description to categorise contacts It should be alphanumeric and should not contain spaces. | - owesMoney - friend |
LESSON_TIME | The day and time of the student's lesson. It should be in format 'day:HH:mm' (e.g. mon:16:00), where 'day' is a three-letter abbreviation (mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun) and time is in 24-hour format (HH:mm) between 00:00 and 23:59. | - wed:13:00 - tue:00:03 |
EDUCATION | The student's education level. It should be alphanumeric and length must be within 1 to 25. | - Primary 2 - Secondary 5 |
INDEX | The index number shown in the displayed list of contacts. It should be a positive integer (1, 2, 3, …) and cannot exceed the number of contacts in the displayed list of contacts. | - 2 - 10 |
GRADE_INDEX | The grade of the student. The grade index ranges from 0 to 4: - 0: Unknown - 1: Failing - 2: Satisfactory - 3: Good - 4: Excellent | - 0 - 3 |
KEYWORD | The keyword specified for find-related commands. Please refer to the section detailing the specific command on how to use KEYWORD appropriately. | N.A. |
DAY | The day specified for finding students in findday. Please refer to the section detailing the specific command on how to use DAY appropriately. | N.A. |
Adding a student: addstudent
Adds a student to the address book.
Format: addstudent n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS lt/LESSON_TIME edu/EDUCATION [t/TAG]…
Tip: A student can have any number of tags (including 0)
Examples:
addstudent n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 134665 edu/primary lt/wed:13:00 t/friend t/colleagueadds a student namedJames Hoto the address bookaddstudent n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/123 Hougang Ave 3 p/1234567 t/dyslexic edu/Secondary lt/tue:00:03adds a student namedBetsy Croweto the address book.
Adding a parent: addparent
Adds a parent to the address book.
Format: addparent n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
Tip: A parent can also have any number of tags (including 0)
Examples:
addparent n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01adds a student namedJames Hoto the address bookaddparent n/Billie e/billie@example.com a/111 Crawfurd Drive p/1234567 t/friend
Editing a contact : edit
Edits an existing contact in the address book.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [lt/LESSON_TIME] [edu/EDUCATION] [t/TAG]…
Notes about edit: Edits the contact at the specified INDEX.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the contact will be removed.
- You can remove all the contact's tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Examples: Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the main list,
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st contact to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd contact to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
Assigning a grade to a student: grade
Assigns a grade to an existing student in the address book.
Format: grade INDEX g/GRADE_INDEX
Notes about grade:
Assigns GRADE_INDEX to the contact at the specified INDEX.
The
GRADE_INDEXranges from 0 to 4:- 0:
Unknown - 1:
Failing - 2:
Satisfactory - 3:
Good - 4:
Excellent
- 0:
Examples:
grade 1 g/1changes the grade of the first contact in the displayed list of contacts toFailinggrade 2 g/4changes the grade of the second contact in the displayed list of contacts toExcellent
Deleting contacts : delete
Deletes the specified contacts from the address book.
Format: delete INDEX [MORE_INDICES]…
Notes about delete: Deletes the contacts at the specified INDEX or INDICES.
Examples:
Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the main list, inclusive of a contact named Betsy,
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd contact in the displayed list of contacts.find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st contact in the results of thefindcommand.listfollowed bydelete 2 3 4 5deletes the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th contacts in the displayed list of contacts.
Caution: When deleting a contact, contacts linked to that contact will be unlinked.
For example, consider a scenario where a parent John has two linked students: James and Betsy.
- If
Johnis deleted, both studentsJamesandBetsywill be unlinked from parentJohn. - If
Betsyis deleted, onlyBetsywill be unlinked fromJohn. The link betweenJohnandJameswill remain intact.
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
Locating contacts by name: find
Finds contacts with names containing one or more of the specified keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Notes about find:
Finds contacts with names containing one or more of the specified KEYWORDS.
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang - Contacts displayed
Examples:
Assuming a list with john, John Doe, Alex Yeoh and David Li
find JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doefind alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
Locating contacts by tag: findtag
Finds contacts whose tags match any of the given keywords.
Format: findtag KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Notes about findtag:
Finds contacts with tags matching any of the specified KEYWORDS.
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
dyslexicwill matchDyslexic - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
dyslexic vegetarianwill matchvegetarian dyslexic - Only full words will be matched e.g.
vegwill not matchvegetarian - Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.vegetarian dyslexicwill return all users with tags containingvegetarianordyslexic
Locating students by lesson day: findday
Finds students who have lessons on specific days of the week.
Format: findday DAY [MORE_DAYS]…
Notes about findday:
Finds students who have lessons on any of the specified DAYS.
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
tuesdaywill matchTuesday - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
tuesday wednesdaywill matchwednesday tuesday - Only full words will be matched e.g.
tueswill not matchtuesday - Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.tuesday wednesdaywill return all students with lessons on Tuesday and students with lessons on Wednesday.
Viewing help : help
Displays a link to the User Guide.
Format: help
Pinning contacts: pin
Pins the specified contacts to the top of the list in the address book.
Format: pin INDEX [MORE_INDICES]…
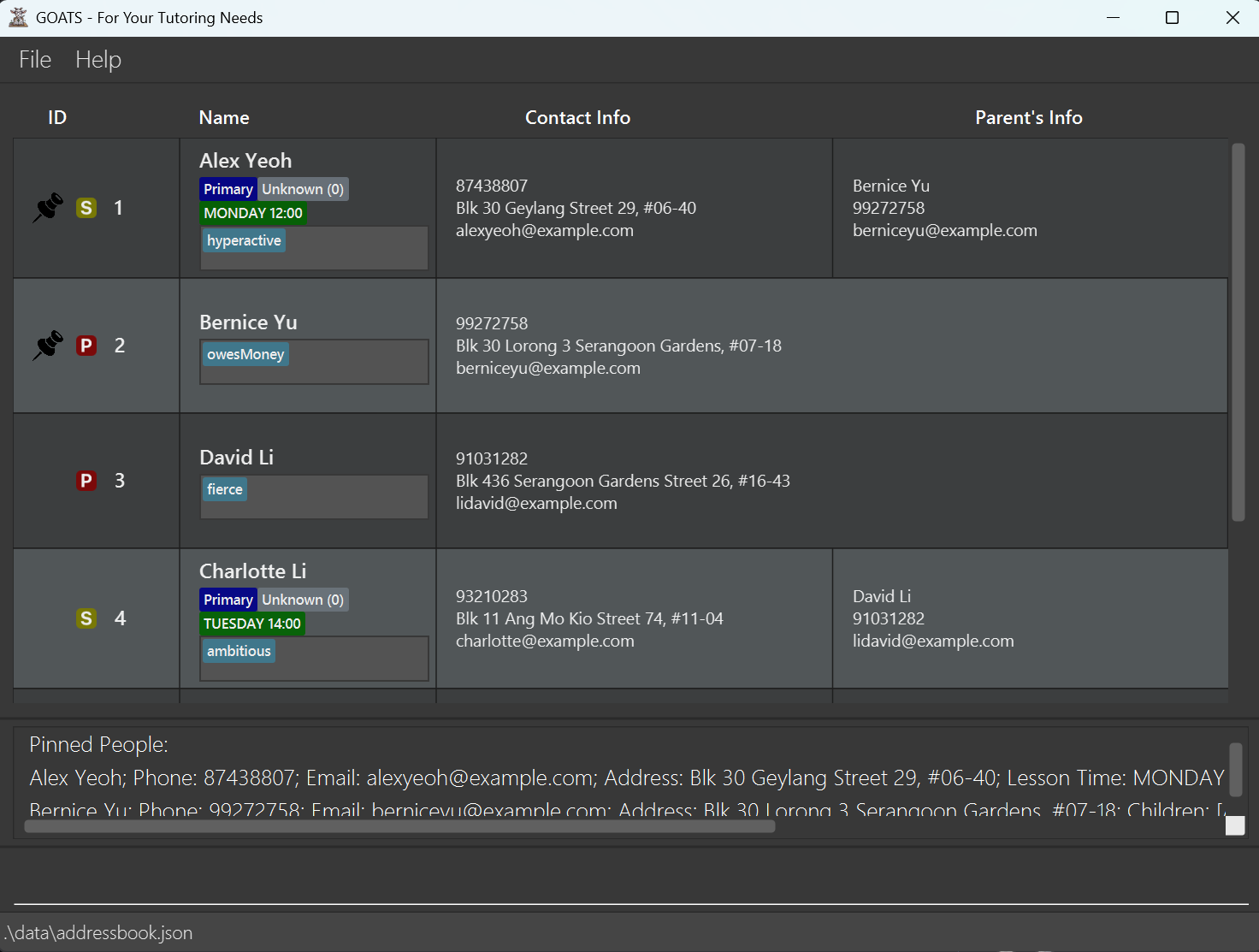
Notes about pin: Pins the contacts at the specified INDEX or INDICES.
- It is possible to pin a pinned contact, however, the contact will not be affected or change by this.
- Pinning contacts may disrupt the initial ordering of the contacts.
- Pinned contacts are indicated by the pin icon.
Examples:
Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the main list, inclusive of a contact named Betsy,
listfollowed bypin 2pins the 2nd contact in the displayed list of contacts.find Betsyfollowed bypin 1pins the 1st contact in the results of thefindcommand.listfollowed bypin 2 3 4 5pins the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th contacts in the displayed list of contacts.
Unpinning contacts : unpin
Unpins the specified contacts in the address book.
Format: unpin INDEX [MORE_INDICES]…
Notes about unpin: Unpins the contacts at the specified INDEX orINDICES.
- It is possible to unpin an unpinned contact, however, the contact will not be affected or change by this.
- Unpinning contacts may disrupt the initial ordering of the contacts.
Examples:
Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the main list, inclusive of a contact named Betsy,
listfollowed byunpin 2unpins the 2nd contact in the displayed list of contacts.find Betsyfollowed byunpin 1unpins the 1st contact in the results of thefindcommand.listfollowed byunpin 2 3 4 5unpins the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th contacts in the displayed list of contacts.
Archiving contacts : archive
Archives the specified contacts in the address book, hiding them from the main list.
Format: archive INDEX [MORE_INDICES]…
Notes about archive: Archives the contacts at the specified INDEX or INDICES.
- It is possible to archive an archived contact, however, the contact will not be affected or change by this.
Examples:
Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the main list, inclusive of a contact named Betsy,
listfollowed byarchive 2archives the 2nd contact in the displayed list of contacts.find Betsyfollowed byarchive 1archives the 1st contact in the results of thefindcommand.listfollowed byarchive 2 3 4 5archives the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th contacts in the displayed list of contacts.
Unarchiving contacts : unarchive
Unarchives the specified contacts in the address book, so that they can be displayed in the main list of contacts.
Format: unarchive INDEX [MORE_INDICES]…
Notes about unarchive: Unarchives the contacts at the specified INDEX or INDICES.
- It is possible to unarchive an unarchived contact, however, the contact will not be affected or change by this.
Examples:
Assuming a list of 7 contacts in the archive list, inclusive of a contact named Betsy,
listarchivefollowed byunarchive 2unarchives the 2nd contact in the displayed list of contacts.find Betsyfollowed byunarchive 1unarchives the 1st contact in the results of thefindcommand.listarchivefollowed byunarchive 2 3 4 5unarchives the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th contacts in the displayed list of contacts.
Listing all contacts : list
Shows a list of all unarchived contacts in the address book.
Format: list
Listing all archived contacts : listarchive
Shows a list of all archived contacts in the address book.
Format: listarchive
Listing students : liststudents
Shows a list of all unarchived students in the address book.
Format: liststudents
Listing parents : listparents
Shows a list of all unarchived parents in the address book.
Format: listparents
Linking a parent to a student : link
Links a parent to a student in a parent-child relationship.
Format: link ch/STUDENT_NAME pa/PARENT_NAME
Notes about link:
Links the student specified by name STUDENT_NAME with the parent specified by name PARENT_NAME.
- The names provided are case-sensitive.
- The names provided must match exactly the names displayed in the address book.
Examples:
Assuming the address book has a student John Doe and a parent Jane Doe,
link ch/John Doe pa/Jane Doelinks the studentJohn Doewith the parentJane Doe
Unlinking a parent from a student : unlink
Removes the parent-child relationship from the specified student.
Format: unlink ch/STUDENT_NAME
Notes about unlink:
Removes the parent-child relationship from the specified student with name STUDENT_NAME.
- The name provided is case-sensitive.
- The name provided must match exactly the name displayed in the address book.
Examples:
Assuming the address book has a student John Doe linked to a parent Jane Doe,
unlink ch/John Doeremoves the parent-child relationship fromJohn Doe
Sorting all contacts alphabetically: sort
Sorts all contacts in the address book alphabetically, keeping pinned contacts at the top of the list.
Format: sort
Tip! Sort can be used to rectify the disarranged list, especially after using the commands pin and unpin.
Notes about sort:
- Pinned contacts will be sorted amongst themselves.
- Unpinned contacts will also be sorted amongst themselves.
- The sorted pinned contacts will be displayed at the top of the list before the sorted unpinned contacts.
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
The GOATS data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
The GOATS data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json.
Caution: If your changes to the data file makes its format invalid, GOATS will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run. Hence, it is recommended to take a backup of the file before editing it. Furthermore, certain edits can cause the GOATS to behave in unexpected ways (e.g., if a value entered is outside the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous GOATS home folder.
Known issues
- When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again. - If you minimize the Help Window and then run the
helpcommand (or use theHelpmenu, or the keyboard shortcutF1) again, the original Help Window will remain minimized, and no new Help Window will appear. The remedy is to manually restore the minimized Help Window.
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Alphanumeric | Text consisting of English letters or/and Arabic numerals |
| Command | An instruction given by the user for the program to perform a certain action |
| Command Line Interface (CLI) | A way to interact with a program by inputting lines of text called command-lines |
| Terminal Emulator | A software that emulates a traditional text-based terminal interface in modern graphical interfaces |
| Graphical User Interface (GUI) | A way to interact with a program which makes use of graphics or visuals as opposed to purely text |
| Home Folder | The main folder where all GOATS-related files will be created and stored |
| Java Archive File (JAR) | A package file that makes it easy to download and launch java-based programs such as GOATS |
| Java | The programming language and platform used to create GOATS |
| JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) | A format for storing data as human-readable text |
| Parameter | Details to be specified for a command. (e.g. When adding a Student to GOATS, the student's name is a parameter) |